It was announced on Wednesday the 4th of July 2012, with a great degree of certainty, that the Higgs Boson was discovered.
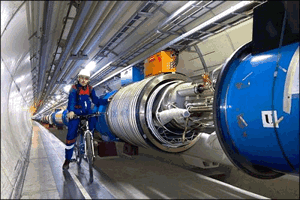
Located near Geneva the Large Hadron Collider(LHC) was built at a cost of A$7 billion. It will accelerate particles to almost the speed of light in two parallel beams before smashing them together in a 27 km tunnel 175 m below the ground. During a ten hour experiment each beam will travel 10 billion km. The energy of each collision will reach 14 trillion electron volts (TeV). This represents an enormous amount of energy, when one considers that the kinetic energy of a flying mosquito is 1.6 X 10-7 joules or one TeV, but the scale is miniscule.
Scientists have observed the behaviour and mass of elemental particles such as the "W" and "Z" particles. It is hard to explain why these elemental particles have so much mass. Scientists have therefore hypothesised the existence of another particle called the Higgs boson that gives rise to mass. By smashing particles together it is hoped to identify theoretical particles such as the Higgs boson that is thought to give rise to mass. The LHC will also simulate the conditions in the expanding Universe shortly after the Big Bang by forming a liquid form of matter called quark-gluon plasma that existed shortly after the Big bang.
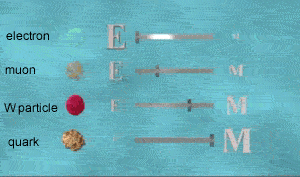
But how does the Higgs field impart mass to particles? Well, the Higgs field is said to be dynamic, made of particles called "Higgs bosons" coming into and out of existence, as shown on the right
How does the Higgs field impart mass. When an electron enters the Higgs field it slips past the bosons with ease. However the quark interacts heavily with the bosons and decreases in speed significantly while the "W" particle has a moderate interaction.
If the hypothesis of Higgs bosons coming in and out of existence is correct it should be possible to create and destroy Higgs bosons and this is one of the primary missions of the Large Hadron Collider. Scientists predict that a direct collision between two protons traveling at the speed of light should force the creation of a Higgs boson.
Play the video on the right for more information.
sourced from https://youtube/tcHz3o4t6Rk
Why did scientists hypothesise the existence of the Higgs boson?
What is the Higgs field?
How does the Higgs field impart mass to elemental particles?
The Higgs field converts into
Which particle has the most energy
Which particle has the most mass
What is the formula that shows that mass and energy are interchangeable?
How will the Large Hadron Collider generate bosons?
Can an elemental particle with large amount of kinetic energy have a high mass as it passes through the Higgs field? Explain.
The boson is a very stable particle.
A proton is a small particle made of one type of solid matter.
A collision between two protons traveling at the speed of light is sure to form a Higgs boson.
A boson can easily be detected by the flash of light it produces.